Depicting the wrist with MRI is challenging, but a new study from Sweden has revealed that 7-tesla MRI improves anatomical visualization and image quality over 3-tesla imaging. This could lead to better detection and management of pathologies.
Injuries to the wrist are difficult to assess noninvasively, due to the wrist's small size and tricky anatomical structures such as intercarpal ligaments, the triangular fibrocartilage complex, and articular cartilage. Costly and invasive surgical interventions such as diagnostic arthroscopy are often necessary, the authors noted in an article published online in European Radiology on 11 August.
At the same time, ultrahigh-field MR systems have become increasingly available for research and clinical purposes, with 7 tesla showing promise for anatomical depiction. But the number of published wrist studies at these higher field strengths remains limited, and this has been compounded by the lack of commercially available, dedicated radiofrequency (RF) wrist coils for 7 tesla. Particularly lacking are studies on 7-tesla wrist imaging with commercially available dedicated coils, the authors noted.
Because improved visualization using noninvasive methods could be of clinical value, a team from Lund University aimed to evaluate visualization of structures at 7-tesla compared with 3-tesla MRI using a dedicated, commercially available wrist coil.
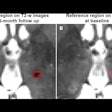
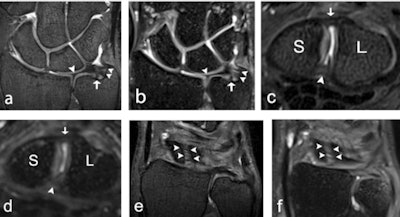 A 32-year-old male healthy volunteer (a, b), a 22-year-old male healthy volunteer (c, d), and a 27-year-old female healthy volunteer (e, f). (a) 7-tesla 0.5-mm-thick coronal 3D proton density (PD) turbo spin-echo (TSE) section and (b) 3-tesla 0.5-mm-thick coronal 3D PD SPACE section with a depiction of the ulnar styloid attachment (arrowheads), the foveal attachment (arrow), and the radial attachment (arrowhead) of the triangular fibrocartilage complex. (c) 7-tesla 0.5-mm-thick axial 3D PD TSE section and (d) 3-tesla 0.5-mm-thick axial 3D PD SPACE section with visualization of the dorsal portion (arrow), and the palmar portion (arrowhead) of the scapholunate ligament. (e) 7-tesla 0.5-mm-thick coronal 3D PD TSE section and (f) 3-tesla 0.5-mm-thick coronal 3D PD SPACE section depicts the dorsal portion of the scapholunate ligament (arrowheads). S = scaphoid; SPACE = "sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolution". All images courtesy of Dr. Simon Götestrand et al. and European Radiology.
A 32-year-old male healthy volunteer (a, b), a 22-year-old male healthy volunteer (c, d), and a 27-year-old female healthy volunteer (e, f). (a) 7-tesla 0.5-mm-thick coronal 3D proton density (PD) turbo spin-echo (TSE) section and (b) 3-tesla 0.5-mm-thick coronal 3D PD SPACE section with a depiction of the ulnar styloid attachment (arrowheads), the foveal attachment (arrow), and the radial attachment (arrowhead) of the triangular fibrocartilage complex. (c) 7-tesla 0.5-mm-thick axial 3D PD TSE section and (d) 3-tesla 0.5-mm-thick axial 3D PD SPACE section with visualization of the dorsal portion (arrow), and the palmar portion (arrowhead) of the scapholunate ligament. (e) 7-tesla 0.5-mm-thick coronal 3D PD TSE section and (f) 3-tesla 0.5-mm-thick coronal 3D PD SPACE section depicts the dorsal portion of the scapholunate ligament (arrowheads). S = scaphoid; SPACE = "sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolution". All images courtesy of Dr. Simon Götestrand et al. and European Radiology."At our institute, hand surgeons and radiologists wanted to investigate whether the higher field strength could improve visualization of wrist ligaments, as current diagnostic imaging often is unsatisfactory when wrist ligament injury is suspected," Dr. Simon Götestrand, lead author and radiologist at Lund University Hospital, told AuntMinnieEurope.com.
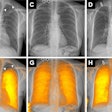
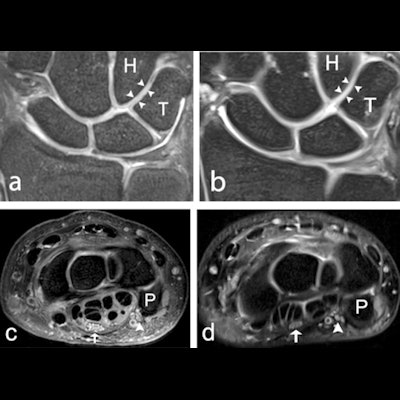
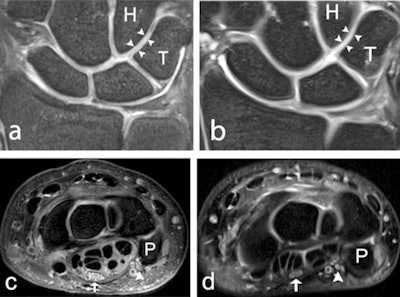 A 39-year-old male healthy volunteer. (a) 7-tesla and (b) 3-tesla coronal 2D PD-weighted section, showing the articular cartilage (arrowheads) between the hamate and the triquetrum. Articular cartilage between other bones is also visible. (c) 7-tesla and (d) 3-tesla axial 2D PD-weighted section, showing the median (arrow), and ulnar nerve (arrowhead), at the level of the pisiform bone. H = hamate; P = pisiform; PD = proton density; T = triquetrum.
A 39-year-old male healthy volunteer. (a) 7-tesla and (b) 3-tesla coronal 2D PD-weighted section, showing the articular cartilage (arrowheads) between the hamate and the triquetrum. Articular cartilage between other bones is also visible. (c) 7-tesla and (d) 3-tesla axial 2D PD-weighted section, showing the median (arrow), and ulnar nerve (arrowhead), at the level of the pisiform bone. H = hamate; P = pisiform; PD = proton density; T = triquetrum.The researchers recruited 18 healthy volunteers (three males and three females from each age decade between 20 and 49 years) and examined them with 7-tesla and 3-tesla MRI. Four musculoskeletal radiologists with 28, 18, five, and 1.5 years of experience underwent a training session before image interpretation to ensure scoring conformity and then graded 2D and 3D images on a five-level visual grading characteristics (VGC) scale for visibility of ligaments, cartilage, nerves, trabecular bone, and tendons, as well as for overall image quality (i.e., edge sharpness, perceived tissue contrast, and presence of artifacts). Scores of 1 indicated "unacceptable," while scores of 4 indicated "good" and scores of 5 indicated "excellent" image quality.
| Anatomical visibility | Image quality |
| Not visible (Score 1) | Unacceptable (Score1) |
| Visible, but with complete loss of detail (Score 2) | Inadequate (Score 2) |
| Visible, with visualization of some anatomical detail (Score 3) | Adequate (Score 3) |
| Visible, with visualization of most anatomical detail (Score 4) | Good (Score 4) |
| Visible, with perfect visualization of anatomical detail (Score 5) | Excellent (Score 5) |
Robust results
The team graded all evaluated anatomical structures, including ligaments, trabecular bone, cartilage, nerves, and tendons, as better visualized at 7 tesla compared with 3 tesla, with an area under the curve (AUCVGC) of 0.62-0.88 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.50-0.97, p = < 0.0001-0.03) using either 2D or 3D imaging. Specifically, 7 tesla was significantly superior to 3 tesla in the evaluation of edge sharpness and perceived tissue contrast. There was no significant difference in grading regarding artifacts. Importantly the results also revealed that MRI of the wrist at 7 tesla with a commercially available wrist coil is feasible at similar acquisition times as for 3 tesla MRI.
| Image quality and anatomical visibility of wrist MRI by field strength* | ||
| 3 tesla | 7 tesla | |
| Ulnar nerve | 6% | 72% |
| Trabecular bone | 56% | 99% |
| Cartilage (2D seq.) | 39% | 79% |
| Foveal attachment of triangular fibrocartilage complex (3D seq.) | 42% | 75% |
| Dorsal portion of LTL (3D seq.) | 19% | 44% |
| Dorsal portion of SLL (3D seq.) | 49% | 69% |
| Edge sharpness | 49% | 90 |
| Perceived tissue contrast | 68% | 90% |
| Artifacts | 74% | 78% |
Limitations of the current study were the small number of subjects and the lack of pathology in the study population. Also, the 3D sequences were optimized for ligament visualization, which may have resulted in a less optimal visualization of other structures. However, the authors underlined that the study demonstrated overall, that wrist structures are better visualized at 7 tesla compared with 3 tesla, this better visibility and delineation likely to translate into better detection and definition of pathology.
Further studies
Discussing the future of wrist imaging, Götestrand noted that the paper's impact on daily practice will be limited for the moment. However, he noted that when ultrahigh-field MR systems are installed at more centers, the work at Lund could inspire greater development of diagnostic musculoskeletal protocols, not just in the wrist but also in the hand, knee, and foot.
"Based on our findings in healthy volunteers, I believe all pathology will be better visualized and delineated at [7 tesla] compared to lower field strengths. To determine whether that is the case, more studies using subjects with suspected pathology need to be carried out," Götestrand said.
The Swedish team is now planning a comparative study on patients with suspected wrist ligament injuries at 3 tesla and 7 tesla, using findings at wrist arthroscopy as the reference standard.