An accelerated breast MRI protocol, performed without contrast media, is comparable to digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) for breast cancer screening, according to a presentation delivered at ECR 2019 in Vienna.
The study results offer the possibility of functional evaluation for breast cancer screening, even without contrast media, said presenter Dr. Valentina Marconi of the University of Udine in Italy.
"Digital mammography is still the gold standard for breast cancer screening, despite important limitations, and the role of DBT is now consolidated [in clinical practice]," she said. "But dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI is the most sensitive modality."
A concern with breast MRI has been that it tends to be costly, require contrast administration, and have long acquisition times. That's why developing an abbreviated breast MR protocol interests researchers. So Marconi and colleagues conducted a study to investigate whether a shortened breast MRI protocol without the use of contrast media -- which they called rapid unenhanced MRI (RU-MRI) -- could be as effective for breast cancer screening as DBT.
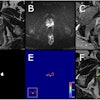
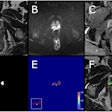
The study included 59 women imaged with both the RU-MRI protocol and DBT between January 2016 and February 2017. Four readers blinded to the patients' clinical history and histology/pathology results reviewed the DBT exams first, followed by the breast MRI exams, categorizing any lesions using the BI-RADS lexicon. The researchers used the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve to evaluate the accuracy of both methods.
The shortened breast MRI protocol consisted of diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) mapping with T1-weighted 1.5-tesla MRI, without contrast. The duration of the RU-MRI protocol was about three minutes, compared with a regular MRI protocol of 20 minutes, Marconi said.
In 118 breasts imaged, 38 cancers were identified, for a disease prevalence of 32%. All cancers were identified by at least one of the four readers. The differences between the area under the curve for the two methods for all readers were not significant (p > 0.05), despite a slight improvement in specificity with the abbreviated breast MRI protocol.
| DBT vs. RU-MRI for breast lesion detection | ||
| Performance measure | DBT | RU-MRI |
| Sensitivity | 84.2%-92.1% | 84.2%-92.1% |
| Specificity | 72.5%-90% | 83.7%-91.2% |
| Positive predictive value | 60%-78.3% | 69%-81.9% |
| Negative predictive value | 92.1%-95.9% | 92.5%-96.4% |
| Accuracy | 80.3%-90.1% | 86.8%-92.2% |
Kappa statistic analysis showed that interobserver agreement among the four readers was good for abbreviated breast MRI (range, 0.618-0.783) and moderate to good for DBT (range, 0.452-0.718).
The study results are promising and offer a starting point for further research, Marconi concluded.
"An abbreviated breast MR protocol makes using the modality for population screening possible," she said.