VIENNA - In times of shrinking hospital budgets, radiology managers have to think even more carefully before deciding to invest in an expensive new system, and they must also try to ensure that any new systems are used cost-effectively. Siemens aims to meet those needs with the two new CT systems that it is showcasing in the European Congress of Radiology's (ECR) technical exhibition.
As part of the company's Agenda 2013 initiative, aimed at meeting the challenges posed by increasing cost pressures in the healthcare market, the company is unveiling the new Somatom Perspective. This 128-slice CT scanner, which features the eMode technology, is designed to reduce the costs of ownership of the technology over its working lifetime, according to Jan Freund, director of global product marketing in Siemens' CT business.
"If you analyze the way that customers set up an examination, they look at image quality and dose, trying to find the most appropriate compromise between those two to get the right diagnostic outcome without putting the patient's health at risk," he explained. "But no customers look at how they can use their system in the most efficient way, in reducing the burden on the generator, bearings, tube, or other components. This system sets the customer's requirements in terms of image quality and dose, and can determine the most efficient way to achieve that while reducing wear and tear on the components. So, for example, it might suggest that with a typical thorax examination taking six or seven seconds, you can reduce burden on the system by extending the scan by half a second and still achieve the same results."
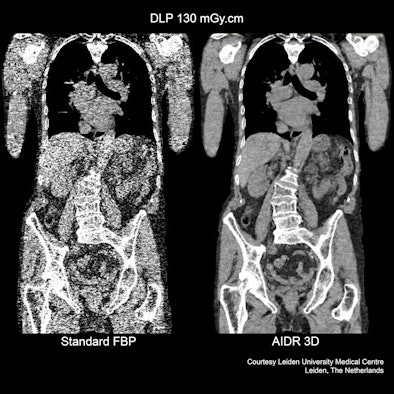 |
| Comparison of Toshiba's AIDR 3D and conventional filtered back projection view of the torso. |
Users will also benefit through a reduction in servicing costs and fewer warranty issues, and those savings can be passed back to the customer, he continued. "We monitor how often customers use the eMode function, and if they stay above a certain threshold of usage -- currently 80% -- then they will receive the benefit of their choice such as a reduction in the cost of the service contract. It is rather like a 'no-claims bonus' on the accident insurance policy for a car," Freund pointed out.
However, Siemens hasn't forgotten its commitment to more traditional forms of technological innovation in radiology. It is exhibiting the Somatom Definition Edge scanner, which has just entered the clinical evaluation phase and should be commercially available later this year. This machine features the company's latest advance in detector technology. In the Stellar Detector, most of the electronic components are incorporated into the photodiode, which significantly reduces electronic noise and improves the signal-to-noise ratio. This allows ultrathin slices of just 0.5 mm to be scanned at very low signal strength, generating images with a spatial resolution of up to 0.33 mm, without the need to increase the radiation dose. Definition Edge is a single-source CT system that can also be operated to give dual-energy examinations, performed consecutively at around half the dose employed in the normal mode, according to the vendor.
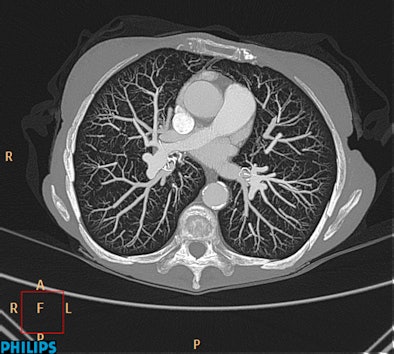 |
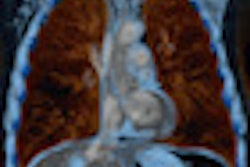
| Ingenuity CT with iDose demonstrates good contrast resolution and visualization of small vascular structures out to the peripheral lung. Image acquired in 6 seconds and reconstructed in 39 seconds. Other scan parameters: 80 kVp, 0.9 mSv, 138 mAs, 32-cm scan length. (Provided by Philips) |
Manufacturers of CT technology face a continuous challenge in setting themselves ever more stringent targets for reducing exposure to potentially harmful radiation. At ECR 2012, Toshiba Medical Systems Europe is introducing two new series of CT scanners incorporating its latest dose reduction technology, AIDR 3D. This Adaptive Iterative Dose Reduction software will be a standard feature on its RXL series, and will be available in a 16 and 32 slice configuration. On its CXL series, it will be available in a 64 and 128 slice configuration. The company has also announced a comprehensive upgrade scheme covering the entire European installed base of Aquilion One, Premium and Prime scanners.
Iterative-based dose reduction software requires extensive computational power, which often results in much longer reconstruction times that limit its clinical usage, especially in those examinations requiring a fast diagnosis. However, the company believes that through a combination of powerful hardware and its new AIDR 3D software its new technology will greatly extend the clinical utility of this approach.
"AIDR 3D is fully integrated in scan protocols for improved workflow, assuring a dose reduction in a clinical setting by up to 75%," noted Henk Zomer, CT business unit manager for Toshiba in Europe. "It offers a substantial noise reduction and improved spatial resolution. We also believe that this is unique software in that produces minimal penalties in reconstruction times, while assuring the best diagnostic image quality at the lowest dose for all patients. AIDR 3D works both in the image and raw data domain and is fully integrated in the exposure control for optimized dose control in all clinical settings, even in emergency departments."
The new system aims to provide benefits in terms of its diagnostic performance, which Toshiba plans to demonstrate at is exhibition stand. Since the software is adaptive, special operator handling is not needed. Automatically optimized iterations assure best image quality for each particular body region, according to Zomer.
Philips is also emphasizing dose reduction and cost-effectiveness in its new technologies displayed in the commercial exhibition. It is showing a new, faster version of its iDose iterative reconstruction technology on its recently introduced Ingenuity family of scanners.
"The addition of the Ingenuity Core and Ingenuity Core128 brings in-room upgradability, allowing customers to get the most value out of their investment and be poised for future growth," says Jamie Valliant, Philips CT product marketing manager. "And now with iDose, customers will not only benefit from improved spatial resolution, advanced clinical capabilities, and improved image quality at low dose, but also will experience even faster reconstruction speeds than before, allowing for quicker results and enhanced productivity and workflow."
Furthermore, iDose is now an option with the Brilliance CT Big Bore. This enables existing CT Big Bore customers to enjoy improvements in image quality at low dose, in addition to the tools available on the scanner today. Philips believes that iDose may offer unique capabilities for radiation oncology to help users reduce radiation exposure during the CT simulation process, while maintaining high image quality, which is important for contouring target volumes and critical structures in radiation therapy planning. The first deliveries of the systems are expected in the second half of 2012.
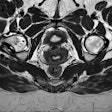
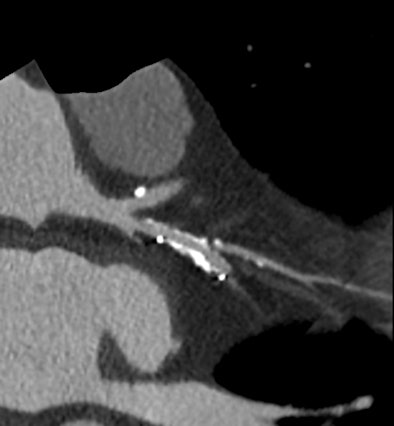 High-definition cardiac CT image obtained on GE Healthcare's Discovery CT750 HD shows stenosis adjacent to stent. (Provided by GE)
High-definition cardiac CT image obtained on GE Healthcare's Discovery CT750 HD shows stenosis adjacent to stent. (Provided by GE)
The company also aims to provide a glimpse into the future of reconstruction by showcasing a radically new iterative model reconstruction technique. Its IMR product is claimed to be a unique model-based, knowledge-based approach that moves CT from data approximation to data restoration. This process is a tremendous leap toward discovering new clinical potentials for CT imaging, the company says.
With its latest technology on display here in Vienna, GE Healthcare aims to tackle some of the specific challenges faced in conducting CT examinations on cardiac patients, including coronary motion, high heart rates, plaque composition, and accurate perfusion. Its Discovery CT750 HD Freedom Edition offers capabilities that could "change the rules" of cardiac CT. Based on the FREEdom (Fast Registered Energies and ECG) technologies, the system is designed to offer major innovations, including intelligent motion correction, improvements in calcium visualization, plaque material composition assessment, and more accurate perfusion calculations.
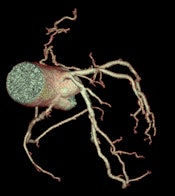 High-definition cardiac CT image obtained on GE Healthcare's Discovery CT750 HD shows bronchial vessels. (Provided by GE)
High-definition cardiac CT image obtained on GE Healthcare's Discovery CT750 HD shows bronchial vessels. (Provided by GE)
With the perennial concerns over the safety of patients during CT examinations, GE Healthcare representatives believe its DoseWatch product can form the cornerstone of a comprehensive, proactive radiation management program. Using data acquired from imaging systems, DoseWatch retrieves, tracks, reports, and monitors the radiation dose delivered to patients during an examination, and presents this data in an organized manner. Multimodality and multimanufacturer, it can be adopted in any imaging program, according to GE.
Providers can assess current practices through the tracking and archiving of dosimetric data, integrated statistical analysis, and connections with the RIS and PACS, enabling optimization and improved dose management over time. Additional features such as automated dose alerts and automated and embedded reports help providers manage dose and overall patient care.
A topic for discussion on Hitachi's booth is the 64 multislice CT system, Scenaria. This is a whole-body scanner with a 0.35-sec rotation speed that reduces dosage and speeds up workflow, while maintaining excellent diagnostic imagery, according to the vendor. The 750-mm aperture can help to maximize patient comfort, reduce anxiety and stress, and facilitate better examinations.
Originally published in ECR Today March 2, 2012.
Copyright © 2012 European Society of Radiology