A team from Tehran, Iran, scooped a prestigious cum laude award from poster-hall judges at RSNA 2016 for its practical and timely work on what interventional radiologists need to know about retinoblastoma.
"Radiologists must be aware of the presentations, the classification, and the imaging features of retinoblastoma and the indications for intra-arterial chemotherapy of retinoblastoma," noted lead author Dr. Hossein Ghanaati, from the department of radiology at Imam Khomeini Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences. "Interventional radiologists should be familiar with the procedural techniques of intra-arterial chemotherapy from puncture to drug injection and the different routs to ophthalmic artery."
Postprocedural follow-up and the patients' outcome after intra-arterial chemotherapy are other vital aspects, he added.
Research goals
In their award-winning e-poster, Ghanaati and his colleagues reviewed the international classification of retinoblastoma, outlined the imaging features across modalities, summarized the indications and technical considerations of intra-arterial chemotherapy, and described the complications of the procedure.
Complications of intra-arterial chemotherapy
- Neutropenia
- Bronchospasm (usually mild)
- Allergy-type reaction
- Thrombocytopenia
- Fever
- Cardiorespiratory side effects
- Injection site complications (e.g., thrombosis or bleeding)
- Epistaxis
- Eyelid edema
- Localized skin erythema
- Madarosis
- Retinal or choroidal vascular occlusions
- Phthisis
- Vitreous hemorrhage
- Ptosis
- Optic nerve swelling
- Retinopathy
- Cranial nerve palsy
- Ophthalmic artery vessel injury or sclerosis
- Suprachoroidal hemorrhage
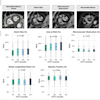
Leukocoria -- or white pupillary reflex, an abnormal white reflection from the retina of the eye -- is the most common, albeit late-presenting, sign in patients with retinoblastoma, occurring in about 60% of cases, they explained. The second major presentation and an early sign of the condition is strabismus, which is found in about 20% of cases. The remaining 20% present with atypical signs, including vitreous hemorrhage, retinal detachment, angle-closure glaucoma, hyphema, pseudohypopyon, iris heterochromia, proptosis, and pseudo-orbital cellulitis.
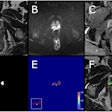
The fundoscopic findings include one or multiple nodular, white or cream-colored masses that are often associated with increased vascularization. There are two types of tumor growth: endophytic growth into the vitreous, causing vitreous seeding, and exophytic growth beneath the retina, causing retinal detachment or seeding.
"On CT, the mass may have inhomogeneous structure with a distinct contour, and it may contain calcifications in 70.5% of cases," the authors stated. "CT scanning has a high sensitivity and specificity (91%) in the detection of intraocular tumors."
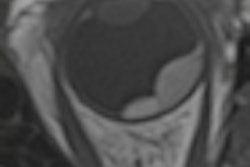
On MRI, retinoblastoma usually demonstrates lower or higher signal intensity than ocular fluid on T1-weighted or fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images, and low signal intensity on T2-weighted images, restricted diffusion, a finding suggestive of high tumor cellularity, and contrast enhancement, they continued. MRI may provide useful information about local tumor extent, especially in the presence of cataracts, vitreous hemorrhage, and optic nerve infiltration.
Furthermore, MRI may be used to assess extraocular and intracranial extension, such as midline primitive neuroectodermal tumors (trilateral retinoblastoma) and leptomeningeal spread. MRI can also depict vitreous and subretinal seeds, providing useful information for classifying the lesion on the basis of the international classification for intraocular retinoblastoma, according to Ghanaati and colleagues.
The essentials: Intra-arterial chemotherapy
The indications of intra-arterial chemotherapy are the failure of conventional management, primary therapy in advanced disease, and bilateral disease.
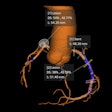
"The ophthalmic artery originates from the internal carotid immediately after its emergence from the cavernous sinus, enters the orbit through the optic foramen, and supplies the orbital contents and the skin above the eyebrow," they wrote. "Its most important branch is the central artery of the retina, which is the sole blood supply to this structure."
As part of the follow-up, a complete blood count with platelets is recommended seven to 10 days after the procedure to monitor for myelosuppresion. Ophthalmic examinations should be performed three or four weeks after treatment and include external examination, visual acuity testing, intraocular pressure measurement, pupil and motility evaluation, and a complete fundus examination under anesthesia with large fundus drawings.
RetCam digital photography and B-scan ultrasonography should be used as objective measures to monitor for a decrease in tumor size, improvement of tumor seeding (either diminution or calcification), and resolution of retinal detachment to determine the effectiveness of individual treatment sessions, they concluded.