Researchers at the Medical Research Council (MRC) in the U.K. have developed a way to significantly shorten MRI scans for people who cannot hold their breath.
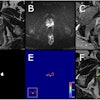
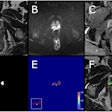
The technique, published online July 28 in Radiology, has reduced breath-hold times from 18 seconds to 4 seconds for scans of the liver in patients with type 2 diabetes.
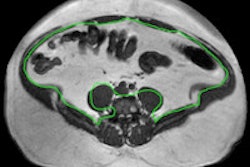
The key to the time reduction is to mathematically compress MR images in a way that's similar to how digital photographs are stored in JPEG files. By doing so, considerably less data are needed to form a detailed view of the liver.
Senior author Kieren Hollingsworth, PhD, and colleagues studied 11 patients with type 2 diabetes, for whom MRI is used to monitor the effect of dietary and physical activity therapy.
The technique needs further testing, according to Hollingsworth, but if validated it could be used for a wider range of organs and disease types to greatly reduce the time required for an MRI scan.