NEW YORK (Reuters Health), Jun 26 - The use of sirolimus-eluting stents (SES) in diabetic patients leads to a significant reduction in in-stent neointimal hyperplasia, compared with that seen when bare metal stents are used. However, a higher rate of incomplete apposition in SES is a concern, Spanish and U.S. researchers report in the June 6th issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
"The most important finding is the high incidence of late acquired incomplete stent apposition observed by intravascular ultrasound at nine-month follow-up in the SES group," Dr. Manel Sabate of Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid told Reuters Health.
Dr. Sabate and colleagues evaluated 75 lesions in diabetic patients who underwent SES implantation and another 65 lesions in patients who received bare metal stents. In all, 117 patients were involved.
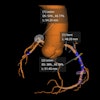
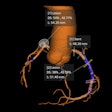
At follow-up, the neointimal hyperplasia mean area in the SES group was significantly reduced compared to that in the bare metal group. The median area was 0.01 square millimeters versus 2.00 square millimeters. This was also true of volume (0.11 cubic millimeters versus 35.3 cubic millimeters).
In addition, say the investigators, stent edges in the SES group showed a significant increase in lumen dimensions mainly due to a significant increase in vessel volume. In those in the bare metal group, there was vessel shrinkage leading to significant lumen reduction.
However, late acquired incomplete stent apposition was seen in 11 lesions in SES group (14.7%) and in none of the patients in the bare metal stent group.
This may be related to late events, such as stent thrombosis, Dr. Sabate said. "Careful clinical follow-up is thus recommended in patients in whom this phenomenon has been detected," he concluded.
Last Updated: 2006-06-23 16:21:52 -0400 (Reuters Health)
J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:2172-2179.
Related Reading
Novel device removes contrast from the coronary sinus, May 22, 2006
Copyright © 2006 Reuters Limited. All rights reserved. Republication or redistribution of Reuters content, including by framing or similar means, is expressly prohibited without the prior written consent of Reuters. Reuters shall not be liable for any errors or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Reuters and the Reuters sphere logo are registered trademarks and trademarks of the Reuters group of companies around the world.