A research group from the University of Groningen in the Netherlands has highlighted findings from whole-body F-18 FDG-PET/CT that show how COVID-19 manifests in critically ill patients.
A team led by Dr. Bram van Leer scanned four mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 with whole-body F-18 FDG-PET/CT imaging to explore reasons for persistent inflammation during the late stages of the disease. The study was published on 12 March in Clinical and Translational Imaging, and underscores the limitations of routine laboratory tests to discriminate inflammation from secondary infections, the researchers noted.
"This case series illustrates the diagnostic potential of F-18 FDG-PET/CT imaging in critically ill patients with persistent COVID-19 for the identification of other causes of inflammation and demonstrates that this technique can be performed safely in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients," the group wrote.
Three of the four patients were scanned between November 2021 and February 2022 after installation of a new long axial field-of-view PET/CT scanner. None of the patients had an obvious source of infection apart from SARS-CoV-2 at the time of the PET/CT exam.
While the pulmonary F-18 FDG radiotracer uptake profile varied between the patients, the PET/CT imaging helped identify heterotopic ossification (abnormal bone growth in nonskeletal tissue), pancreatitis, and gastritis, the investigators reported.
In one case, a 26-year-old pregnant woman was admitted because of mild respiratory failure due to COVID-19 and premature contractions. She underwent a C-section. Two days later, she had an episode of insufficient respiratory function and was intubated. Due to this second episode of respiratory decline, the F-18 FDG-PET/CT was performed.
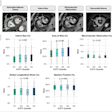
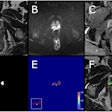
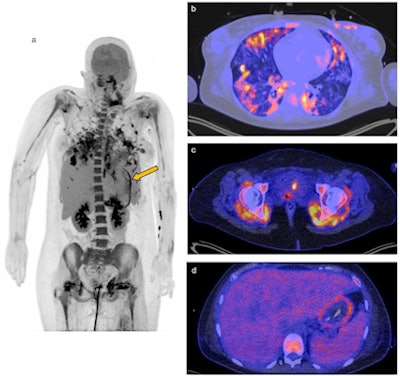 F-18 FDG-PET/CT of a 26-year-old woman with COVID-19. (A) Maximum intensity projection. Physiological uptake in the kidneys and liver. Reduced uptake in the brain due to sedation. Reactive bone marrow. The yellow arrow points toward the uptake in the gastric wall. (B) Transaxial fusion PET/CT image of the lungs with ground-glass opacities and some consolidations on CT, characteristic for COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Heterogenous uptake of F-18 FDG radiotracer. CT in lung setting. (C) Transaxial fusion PET/CT image of the hips with high uptake in the posterior lateral and medial muscle of the hip at both sides. CT in soft tissue setting. (D) Transaxial fusion PET/CT image of the abdomen with clear tracer uptake in the gastric wall. SUV-bw threshold of 5.00 α = 50%. Image and caption courtesy of Clinical and Translational Imaging through CC BY 4.0.
F-18 FDG-PET/CT of a 26-year-old woman with COVID-19. (A) Maximum intensity projection. Physiological uptake in the kidneys and liver. Reduced uptake in the brain due to sedation. Reactive bone marrow. The yellow arrow points toward the uptake in the gastric wall. (B) Transaxial fusion PET/CT image of the lungs with ground-glass opacities and some consolidations on CT, characteristic for COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Heterogenous uptake of F-18 FDG radiotracer. CT in lung setting. (C) Transaxial fusion PET/CT image of the hips with high uptake in the posterior lateral and medial muscle of the hip at both sides. CT in soft tissue setting. (D) Transaxial fusion PET/CT image of the abdomen with clear tracer uptake in the gastric wall. SUV-bw threshold of 5.00 α = 50%. Image and caption courtesy of Clinical and Translational Imaging through CC BY 4.0."A gastritis was found as a possible secondary infection focus," the researchers wrote. "The patient was still SARS-CoV-2 positive at the time of F-18 FDG-PET/CT."
The patient was referred to another hospital the day after the PET/CT and was weaned from mechanical ventilation 13 days later, they added.
Interestingly, all four patients showed muscle radiotracer uptake around the hips and/or shoulders, according to the findings.
"This is especially interesting since two of those patients were deeply sedated, therefore active muscle use, explaining physiological F-18 FDG uptake, would have been unlikely," they wrote.
Ultimately, F-18 FDG-PET/CT data in critically ill patients are rare and this case series increases available limited knowledge on the approach, the researchers wrote.
"Although larger series are needed, and this single-center case series does not provide generalizable conclusions, it illustrates the potential of F-18 FDG-PET/CT imaging in ICU patients with (persistent) COVID-19 ARDS," the group concluded.