The European Association of Nuclear Medicine Research (EARL) and Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers Alliance (QIBA) have signed a deal that looks set to have implications for nuclear medicine cancer clinical studies and practice.
Through the agreement, the two organizations will work together on PET/CT research and develop a proposal to submit to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for wider implementation of PET/CT as an imaging biomarker in clinical trials.
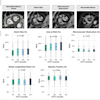
In a first pilot study, nine clinical sites across Europe and Japan have passed the conformance test for the alliance's FDG-PET/CT profile, meaning they are conducting best practices and the uptake of radiopharmaceuticals can be measured reliably at these centers of excellence.
This could help many cancer patients and those with COVID-19 or long-COVID, according to the EARL and QIBA.
The European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM) launched the EANM Research initiative in 2006. One of the main objectives of the program has been promoting multicenter nuclear medicine and research. In 2010, the FDG-PET/CT accreditation program was created in order to address variability in the quickly growing field of quantitative FDG-PET imaging by setting up guidelines and specifications to which the participating sites must adhere.
From 2010 until July 2016, the EANM Research FDG-PET/CT accreditation program has collected over 2,500 phantom datasets from approximately 200 systems and 150 imaging sites worldwide.