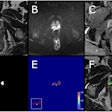
NEW YORK (Reuters Health), May 29 - Three-dimensional MRI using a 3-tesla system appears to be reliable and more accurate than transesophageal echocardiography for revealing aortic high-risk plaques in acute stroke patients, German researchers report in the May issue of the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry.
"3D MRI," lead investigator Dr. Andreas Harloff told Reuters Health, "provided a high sensitivity for the detection of aortic high-risk sources of cerebral embolism."
It was demonstrated "that 3D MRI is a promising tool for the detection of high-risk plaques in patients with undefined stroke etiology -- cryptogenic stroke -- despite extensive routine diagnostics including transesophageal echocardiography," he said.
Harloff and colleagues at University Hospital Freiburg used both methods to examine 74 acute stroke patients. MRI detected plaques in 50% of the patients compared with 31.1% of patients using echocardiography. The number of high-risk plaques detected by MRI was also substantially higher than that with echocardiography (74 versus 47, respectively).
In addition, MRI detected aortic high-risk sources of brain ischemia in eight of 26 patients with cryptogenic stroke, which were not found during standard diagnostics.
Harloff pointed out: "The detection of additional aortic high-risk pathologies by 3D MRI has the potential to guide and thus improve the prevention of recurrent stroke."
Nevertheless, he and his colleagues conclude that "before this novel MRI technique can be generally recommended, its diagnostic value needs to be evaluated rigorously at various imaging sites."
In an accompanying editorial, Dr. Emmanuel Touze of Centre Hospitalier Sainte-Anne, Paris, agrees and concludes that "despite some limitations, the results of this work are important because they show the feasibility of the technique and give us new insights into what can be done in this field."
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2008;79:489,540-546.
Last Updated: 2008-05-28 16:01:06 -0400 (Reuters Health)
Related Reading
4D MRI enables blood-velocity measurement in mitral valve insufficiency, June 24, 2005
Copyright © 2008 Reuters Limited. All rights reserved. Republication or redistribution of Reuters content, including by framing or similar means, is expressly prohibited without the prior written consent of Reuters. Reuters shall not be liable for any errors or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Reuters and the Reuters sphere logo are registered trademarks and trademarks of the Reuters group of companies around the world.