Research teams from across Belgium have joined forces to create an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm that evaluates CT scans of patients admitted to the hospital with COVID-19.
The resulting icolung algorithm, cloud-based AI software used to quantify disease burden in COVID-19 patients on non-contrast chest CT, is intended for clinical use in quantifying lung pathology from chest CT scans. It is the result of a collaboration between software developer Icometrix, Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), and other institutions.
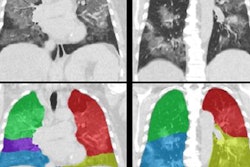
Evaluating the type, pattern, and extent of lung pathology on chest CT can help in the assessment, triage, and follow-up of COVID-19 patients, according to the group. Triage can help alleviate the increasing burden on intensive care units and allocate resources. icolung has the potential of further decreasing workload in clinical practice by providing a fully automated assessment of the total and lobar disease burden, they said.
The algorithm can quantify total and regional lesion burden and returns a concise report and annotated images directly into the hospital PACS within 10 minutes, the researchers added. The icolung software integrates into the hospital PACS and is currently offered pro bono, they noted.