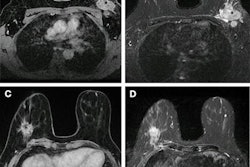
In an AI blog posting released on 28 September, the European Society of Radiology (ESR) has promoted the findings of important research that reported MRI radiomics features are associated with the tumor characteristics occurring in cases of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
In the retrospective analysis, MRI radiomic features significantly correlated with protein expression of CD3 and immunotherapy target PD-L1. The authors also found numerous correlations between radiomics features and RNA expression levels.
The study was published on February 21 in European Radiology. It was led by Stefanie Hectors, PhD, from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City.
The study included patients with HCC who had MRI performed before surgery. It aimed to evaluate whether MRI could be used as a noninvasive method to characterize HCC lesions, an important step for matching patients with new types of targeted treatments.
Typically, characterizing HCC tissue requires invasive tissue sampling as well as specialized equipment and expertise, the ESR noted. The findings suggest MRI radiomics may also be used to predict immune-oncological features of HCC, but more studies are needed to validate the results.