Parkinson's disease, a progressive disorder of the nervous system, affects more than six million people worldwide. It is characterized by symptoms including slowness of movement, rigidity, and tremor. A new study from researchers in Spain and the U.S. suggests that focused ultrasound could be beneficial for patients with asymmetric Parkinson's disease, in which symptoms are much more severe on one side of the body.
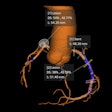
Focused ultrasound is an emerging therapy that offers a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgical approaches. It works by focusing multiple ultrasound beams onto targets deep within the body, with MRI used to monitor and guide the procedure in real-time. The focused sonic energy at the target point can be used to destroy unwanted tissue or interrupt faulty brain circuits.
In a randomized, double-blinded trial, the study team -- from Centro Integral de Neurociencias HM CINAC and the University of Virginia Health Sciences Center (UVA Health) -- evaluated the use of focused ultrasound in 40 patients with Parkinson's disease. All had symptoms not fully controlled by medication or were ineligible for deep-brain stimulation, the main type of surgery used to treat Parkinson's.
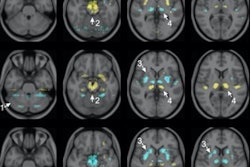
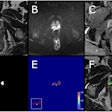
The researchers assigned 27 participants to receive focused ultrasound, while 13 others underwent a sham delivery procedure. The focused ultrasound was targeted onto the subthalamic nucleus in the patients' brains, on the side opposite to their main motor signs. The subthalamic nucleus is the neurosurgical target usually used for deep-brain stimulation treatments. In this trial, focused ultrasound was used instead to create the therapeutic lesions.
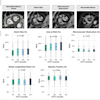
The study assessed participants' motor symptoms before and after the procedure on a scale of 1-44 (using the Movement Disorder Society-Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale motor score), with higher scores indicating greater impairment. In the group treated with focused ultrasound, the mean score for the more affected side decreased from 19.9 at baseline to 9.9 at four months. In the control group, the score changed from 18.7 to 17.1.
 Dr. Jeff Elias. Photo courtesy of UVA Health.
Dr. Jeff Elias. Photo courtesy of UVA Health."This small brain region, the subthalamic nucleus, had a very strong and potent effect on parkinsonian symptoms when we targeted it with precise, focused ultrasound energy," said Dr. Jeff Elias, a neurosurgeon at UVA Health.
Elias notes that clinical adoption of this focused ultrasound procedure will require further technology refinements to ensure reliability and safety. With this in mind, the researchers examined the safety of the new approach by assessing procedure-related complications four months after treatment. Side effects in the active-treatment group included involuntary muscle movements, muscle weakness on the treated side, and speech and gait disturbances. In most cases, these were temporary, but in six patients, some effects persisted a year later.
The study findings were published on 24 December in the New England Journal of Medicine. First author Dr. Raúl Martínez-Fernández, Ph.D., and colleagues concluded that these results warrant additional larger studies conducted over longer periods of time.
Tami Freeman is an online editor for Physics World.
The comments and observations expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of AuntMinnie.com.
© IOP Publishing Limited. Republished with permission from Physics World, a website that helps scientists working in academic and industrial research stay up to date with the latest breakthroughs in physics and interdisciplinary science.