NEW YORK (Reuters Health), Jun 29 - What appears to be a blue nevus might be a cutaneous melanoma metastasis. High-resolution ultrasonography can help dermatologists make the diagnosis, a team in Tours, France, has shown.
The finding was reported online June 19 in the British Journal of Dermatology by Dr. Mahtab Samimi, at Universite Francois Rabelais, and colleagues.
Employing this technique "could prevent some skin biopsies," Dr. Samimi commented by e-mail. However, high-resolution ultrasonography is not as widely used in dermatology practices as it might be. "For the moment it is not currently used because of its cost (30,000 euros). Besides, HR ultrasonography is not reimbursed yet by the Health Assurances -- at least in European countries."
While most blue lesions can be diagnosed correctly by visual assessment, they explain, differentiating them from cutaneous metastases of melanoma can be difficult. To be safe, a blue lesion is usually excised in patients with a history of malignant melanoma. "A tool that could help to discriminate between these two similar lesions would be valuable, avoiding unnecessary excision of blue nevi," the researchers point out.
To investigate the value of high-resolution ultrasonography in this regard, Dr. Samimi and associates studied 29 patients with 39 blue skin lesions. Seventeen patients had a history of melanoma.
The lesions were studied with dermoscopy and high-resolution ultrasonography before excision. Based on the histologic diagnosis as reference, the specificity of sonography was 94.0%, compared to 77.4% for clinical examination and 73.7% for dermoscopy.
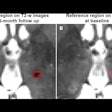
The ultrasonographic images could be differentiated quite readily, the authors report. "A blue nevus is a homogeneous, hypoechoic, 'dish'-shaped lesion, located in the superficial dermis, whereas metastases of melanoma are 'egg'-shaped or 'potato'-shaped, hypoechoic, heterogenous lesions, located in the hypodermis."
While skilled examiners can usually identify a melanoma metastasis correctly, Dr. Samimi and colleagues say that ultrasound "should assist the decision to remove or to leave the lesion when a patient has a history of melanoma."
http://link.reuters.com/neg64m
Br J Dermatol 2010.
Last Updated: 2010-06-28 14:52:10 -0400 (Reuters Health)
Related Reading
'Incurable' skin cancers may be amenable to radiation plus stem cell transplant, April 6, 2010
RT for high-risk melanoma patients reduces lymph node recurrence, November 3, 2009
US can predict survival of melanoma patients, September 25, 2009
Copyright © 2010 Reuters Limited. All rights reserved. Republication or redistribution of Reuters content, including by framing or similar means, is expressly prohibited without the prior written consent of Reuters. Reuters shall not be liable for any errors or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Reuters and the Reuters sphere logo are registered trademarks and trademarks of the Reuters group of companies around the world.