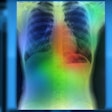
An artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm can provide a promising level of accuracy for diagnosing heart failure on chest radiographs, according to a presentation from Japanese researchers at the recent European Society of Cardiology (ESC) virtual congress.
Using chest x-rays from a publicly available database, a team of researchers led by Takuya Matsumoto of the University of Tokyo trained a deep-learning algorithm that yielded 82% accuracy for detecting heart failure on a test dataset.
"Deep learning is useful for diagnosing heart failure on x-ray images," Matsumoto said.
Although deep-learning algorithms for detecting pulmonary nodules and cardiomegaly on chest x-rays has been reported in the literature, research on applying the models for diagnosing heart failure remains scarce, according to Matsumoto.
To develop their own deep-learning algorithm for this task, the group first gathered 870 chest x-rays from the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) ChestX-ray8 database. Of these, 425 were normal and 445 were from patients with heart failure.
All of these cases were then checked and relabeled by two cardiologists, according to Matsumoto. Consequently, 190 normal cases and 92 heart failure cases were discarded from the study due to incorrect labeling. For the purposes of this study, heart failure was defined as cardiomegaly and congestion in a chest x-ray with a cardiothoracic ratio of over 50% or radiography presence of pulmonary edema, Matsumoto said.
Of the remaining cases, 210 normal cases and 328 heart-failure cases were used to train the deep-learning algorithm. Validation was then performed on 25 normal cases and 25 heart-failure cases.
Initially, the algorithm could only achieve 63.5% accuracy. But after data augmentation to increase the sample size and transfer learning techniques were utilized, the algorithm's accuracy increased to 93.9% on the training test set and 92% on the validation set. In addition, it produced strong results on the test set:
- Sensitivity: 75%
- Specificity: 94.4%
- Accuracy: 82%
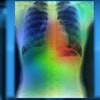
"Also, the [algorithm's heat maps show] us that the machine is now able to recognize the lung field and the heart in the same way that as we humans do," Matsumoto said.
He noted that a 2018 study in the literature found that deep learning yielded 87.3% accuracy for detecting cardiomegaly on chest x-rays.
"Considering small sample size and the difficulty of detecting heart failure compared to cardiomegaly, this study can be said to have achieved a similar level of accuracy as the previous one," he said.
In the future, the researchers plan to develop a program that can classify images into more detailed categories by incorporating more clinical information such as echocardiograms or laboratory data.