Dear Imaging Informatics Insider,
Are you sure your imaging equipment is protected from a cyberattack? If not, now would be a good time to review your institution's cybersecurity practices. A new hacker group called Orangeworm has developed a computer virus designed specifically to target the healthcare sector, and x-ray and MRI machines have already been infected, according to a warning issued this week by antivirus firm Symantec.
How does the virus attack its targets and what can healthcare institutions do to protect themselves? Click here to find out.
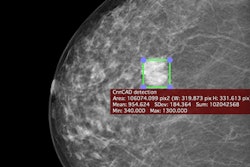
Can computer-aided detection (CAD) software based on a deep-learning algorithm accurately detect as well as characterize lesions on mammography studies? Yes, it can, according to Hungarian researchers.
In an article published online in Scientific Reports, the researchers shared how their deep-learning algorithm was able to take second place in a large artificial intelligence (AI) challenge aimed at improving risk stratification in screening mammograms. The algorithm performed even better in testing on a different database, yielding 90% sensitivity on a per-lesion basis and only 0.3 false-positive marks per image. Click here for all the details.
Meanwhile, a Spanish group has developed a tool in its clinical decision-support system to control repeated requests for imaging studies. The team found that more than 5% of imaging studies ordered over 12 months generated an alert notifying the ordering physicians that their request had been previously performed on the patient within the last 180 days. After viewing the alert, the ordering providers elected not to proceed with more than one-third of the initial requests. Get the full details here.
In other news, the U.K. Royal College of Radiologists has updated its advice for healthcare professionals providing reports on imaging investigations. The 17-page document includes guidance on teleradiology, home reporting, and AI-assisted reporting. Click here to learn more and to download it for free.
A team of researchers from Greece found a deep-learning algorithm that analyzes B-mode morphological ultrasound data and patient demographic information can classify the severity of liver fibrosis in cases of chronic liver disease. Click here to find out how this assessment could be useful for inexperienced users.
ECR 2018 featured a significant increase in AI-oriented educational content, ranging from fascinating talks on big-picture issues, as well as a plethora of presentations on the latest research. For example, AI can also help detect and characterize disease, such as differentiating lung nodules on CT scans. It can also enable semiautomated detection of radiographs.
You'll also want to check out our video interviews with Wiro Niessen, PhD, on how AI can help you; Dr. Sergey Morozov, PhD, on tapping AI's potential; and ECR 2018 President Dr. Bernd Hamm on the impact of AI. Another session at the Vienna congress highlighted the terrifying possibilities of a cyberattack on imaging equipment.
If you have any tips or suggestions for topics you'd like to see covered in the Imaging Informatics Community, please feel free to drop me a line.