Oxipit's ChestEye artificial intelligence (AI) software helped detect more clinically relevant lung nodules, potentially identifying early cancer diagnosis, according to a study from Oxipit and AstraZeneca.
To study the software, it was deployed at two primary care centers in Lithuania. Approximately 50,000 chest x-rays were analyzed throughout 2021. The software analyzes chest x-rays and corresponding radiologist reports to identify any unreported findings. These missed findings are then validated by an Oxipit radiologist. Validated missed findings are then highlighted in the x-ray and a reporting radiologist is notified to take another look at the study, according to the companies.
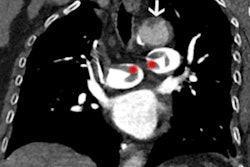
Over the course of a year, the software identified 190 clinically relevant missed findings, 82 of which were potentially missed subtle pulmonary nodules. Most of the nodules in the Oxipit studies are subtle, measuring less than 15 mm and often partially obscured by superposing structures, including rib and heart shadows.
Launching a nationwide ChestEye Quality deployment in Lithuania would help to identify up to 20% of early lung cancer instances annually, according to the study.
AstraZeneca is a founding member of Lung Ambition Alliance, a partnership of organizations that aims to eliminate lung cancer as a cause of death.