Dr. Alexis Jacquier, PhD, a radiologist at the Center for Magnetic Resonance in Biology and Medicine, Aix-Marseille University, is the vice president of the French Society of Cardio-Vascular Radiology (Société Française d'Imagerie CardioVasculaire, SFICV). In this interview, he discusses the updated training scheme that will take effect for all this year's 254 French radiology residents and explains about how artificial intelligence (AI), dose optimization, and the structured report will be covered.
What is changing in France's new training scheme?
Jacquier: The reform is a substantial improvement in the training scheme, as it now better reflects daily routine, and especially cardiac imaging. Today, cardiac imaging is used on a daily basis, and any physician can prescribe an imaging study. Oncologists can prescribe cardiac imaging for pre- and postchemotherapy evaluation; diabetologists use calcium scoring to adapt cardiovascular prevention strategy, and so on.
 Dr. Alexis Jacquier, PhD, from Aix-Marseille University.
Dr. Alexis Jacquier, PhD, from Aix-Marseille University.To make sure they have a complete vision of modern radiology practice, residents will now undergo a three-step training, which will include base training with a focus on emergency radiology; in-depth training to cover every subspecialty; and consolidation training to provide specific skills for one or two subspecialties.
Every subspecialty society is responsible for subspecialty e-learning material, to ensure homogeneous teaching and training across the country. The SFICV started recording sessions with French experts last week for training phase 1 and 2. The series will be freely available to residents on the French Council of the Teachers of Radiology website and to all radiologists on the French Society of Radiology website in November 2018. A series on the structured report will be available as well, linking with the e-learning content.
What should the structured report include?
Radiologists must use generic terms that any other physician can understand. Digital values help referring physicians to navigate through the imaging report all the way to its conclusion. For cardiac imaging, we added key points, for instance CAD-RADS (coronary artery disease reporting and data system classification) in myocardium segment localization.
With the structured report, we'll be able to collect the information and homogenize imaging interpretation nationally. Healthcare authorities are not always aware of the value of examinations such as coronary CT. So if you're able to show how many coronary CT scans have been performed over a year -- and for what indication and implication for patient care -- you can help them get an idea.
The possibilities offered by AI will transform the way we write our reports. AI will potentially enable to spot identical terms, for instance stenosis, narrowing, and overload, in the report, and to automatically or semiautomatically analyze interesting or potentially interesting information.
The structured report will develop considerably in the future. Right now all radiologists write their reports in their own words and it's complicated to get all the information.
What are the applications of AI in cardiac imaging?
Machine learning works really well for automatic contour detection. Many systems can reliably distinguish the right from the left ventricle. AI will help the radiologist in posttreatment validation, by expediting that phase from currently five to 15 minutes to 30 seconds for an examination.
AI will also potentially help in research and many people are working in that field. The media has helped convert it into a hot topic. However, we should remain cautious as to our expectations. AI will change the way we work, but probably not how we expect.
What are the new developments in dose reduction?
Radioprotection is the first chapter of the new training scheme and a key point at the end of training too. Radiologists must validate their skills and update their knowledge of radioprotection every 10 years.
Dose reduction is a crucial aspect of our practice. In France, we are lagging behind in MR equipment. But we acknowledge the effort made by CT constructors to provide new equipment that achieves better results with lower irradiation dose.
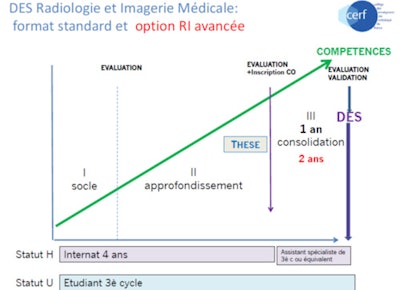 Specialist studies diploma (diplôme d'études spécialisées, DES) in radiology and medical imaging: standard format and advanced training reform option.
Specialist studies diploma (diplôme d'études spécialisées, DES) in radiology and medical imaging: standard format and advanced training reform option.Reducing dose is made easier with modern equipment and image reconstruction algorithms. We also use DACS (dose archiving and communication system) to collect patient dose information and limit radiation exposure.
What about contrast agent use in cardiac imaging?
We can perform MR examinations and preserve image quality by using half the usual contrast agent dose (0.1 mmol/kg instead of 0.2 mmol) and modifying image acquisition parameters.
Some sequences do not even require contrast media use; for example T1 and T2 mapping sequences can give values on myocardium signal (transverse or longitudinal relaxation time), enabling to make a diagnosis without injecting any contrast media. For CT, new technology enables to decrease acquisition time and subsequently contrast media dose.
An increasing number of studies show that contrast is not necessary for myocardium pathology diagnosis. It's not in the guidelines yet, but awareness of our restrictions with chelated gadolinium use is growing.
Were there any relevant sessions held at the French national congress of radiology, JFR 2018?
Yes, the French Society of Radiology and SFC (French Cardiac Society) organized sessions about cardiac imaging. Also, an announcement was made on Friday afternoon, the CERF president spoke about training reform, and there was a session on Sunday about teaching in medicine by 2020. Click here for more details.