EuroMinnies finalists, page 2
Scientific Paper of the Year
Coronary CT angiography and 5-year risk of myocardial infarction. The SCOT-HEART investigators, New England Journal of Medicine, September 2018.
In a follow-up study of the Scottish Computed Tomography of the Heart (SCOT-HEART) trial, researchers from various institutions in the U.K. and Ireland examined the five-year outcomes of more than 4,000 patients whom clinicians had referred for chest pain assessment at one of 12 cardiology centers.
The authors found that patients with chest pain who underwent coronary CT angiography (CCTA) with standard care had a markedly lower rate of myocardial infarction or death from coronary artery disease than those who only received standard care in a new study. CCTA in addition to standard care was associated with a 41% lower subsequent risk of nonfatal myocardial infarction or death from coronary artery disease than standard care alone.
"The use of [CCTA] resulted in more correct diagnoses of coronary heart disease than standard care alone, which, in turn, led to the use of appropriate therapies, and this change in management resulted in fewer clinical events," wrote first author Dr. David Newby, from the University of Edinburgh, and colleagues. "The more general message from these trials is that the information provided by a diagnostic test can resonate therapeutically beyond making a correct diagnosis of coronary artery disease and that clinicians should aggressively pursue preventive measures to achieve the best outcomes possible while minimizing daily symptoms."
More details on this paper are available in our news report.
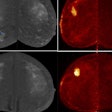
One-view breast tomosynthesis versus two-view mammography in the Malmö Breast Tomosynthesis Screening Trial (MBTST): A prospective, population-based, diagnostic accuracy study. Zackrisson S et al, Lancet Oncology, November 2018.
This Swedish study included almost 15,000 women screened over a period of five years who first underwent two-view digital mammography screening and then one-view digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) with reduced compression during another visit. DBT with a single view detected over a third more (34%) breast cancers than traditional mammography, and most of the breast cancers were invasive cancers.
DBT demonstrated a higher sensitivity at 81.1% versus 60.4% for digital mammography, according to lead author Dr. Sophia Zackrisson, an associate professor at Lund University and a radiologist at Skåne University Hospital in Malmö.
To simplify breast cancer screening using DBT, the prospective, population-based Malmö trial investigated single-view DBT (mediolateral oblique view) compared with conventional two-view digital mammography.
"This strategy minimizes the radiation dose to women undergoing breast cancer screening and reduces the extent of screen-reading compared with dual-imaging methods," Zackrisson and colleagues wrote. "If supported by cost-effectiveness studies, one-view digital breast tomosynthesis warrants consideration as the preferred breast cancer screening method in the future."
Get more details in this article.
Best New Radiology Device
Logiq E10 ultrasound scanner, GE Healthcare
Introduced at ECR 2018, Logiq E10 is GE's flagship ultrasound scanner for radiology, shared services, and other clinical applications outside of the cardiology and ob/gyn segments. The vendor is positioning the machine as its most advanced radiology ultrasound scanner ever, built from the ground up to support the emerging integration of artificial intelligence and medical imaging.
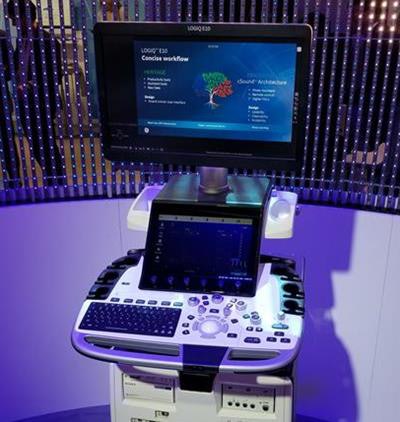 Logiq E10 ultrasound scanner.
Logiq E10 ultrasound scanner.The system uses GE's cSound Architecture platform, which acquires and reconstructs data in a manner similar to an MRI or CT system, according to the company. That requires a lot of data processing power, so GE built graphics processing units (GPUs) from NVIDIA into Logiq E10. These GPUs will also enable E10 to support the growing use of artificial intelligence algorithms to analyze ultrasound images, according to GE.
Other features on Logiq E10 include a Photo Assistant App that allows users to photograph relevant anatomy and attach photos to clinical images that are sent to radiologists in DICOM format. Another tool, Remote Clinical Application, enables users to manipulate scanner settings with a remote control on their tablet or smartphone. Cloud connections are made available via Tricefy from Trice Imaging.
Logiq E10 began shipping globally shortly after its ECR introduction. Learn more in our article.
Magnetom Sola 1.5-tesla MRI scanner, Siemens Healthineers
The 1.5-tesla Magnetom Sola MRI scanner also was unveiled at ECR 2018. In addition to the BioMatrix Respiratory Sensor that was included on Magnetom Vida, the new system benefits from two new BioMatrix sensors: Beat Sensor and Kinetic Sensor.
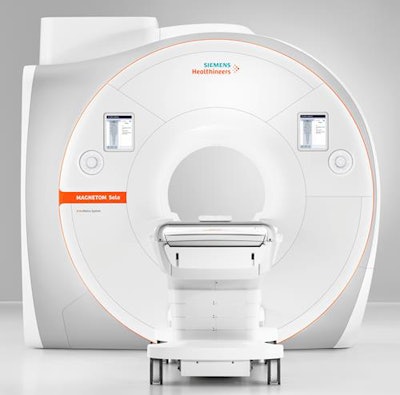 Magnetom Sola 1.5-tesla MRI scanner.
Magnetom Sola 1.5-tesla MRI scanner.Beat Sensor is integrated into the scanner's new body coil and is designed to automatically capture heart motion in real-time and help trigger sequences based on the cardiac rhythm. Similarly, Kinetic Sensor is an in-bore camera system that recognizes a patient's head motion in real-time, then adjusts the MRI scan based on the real-time motion information. As a result, it yields a significant reduction in artifacts and higher diagnostic image quality, while avoiding rescans, Siemens said.
Magnetom Sola has a new magnet with higher homogeneity than the company's other 1.5-tesla scanner, Magnetom Aera. It also offers a higher field-of-view -- 50 x 50 x 50 cm -- as well as a new gradient system and coils, and comes with a number of other applications designed to speed up and automate routine exams.
Sola's Simultaneous Multi-Slice technology, which can acquire multiple slices in parallel, can now be utilized in turbo spin-echo sequences, Siemens said. As a result, the scanner can offer acquisition time savings of as much as 46% for musculoskeletal examinations, according to the company.
You can find out more in our report from ECR 2018.
Best New Radiology Software
Breast screening artificial intelligence software, Kheiron Medical Technologies
Kheiron Medical Technologies' deep-learning breast cancer screening software offers users a second read for mammography images in a screening setting. It has the potential for reading screening mammograms and acting like an independent reader, according to the vendor.
The company received the CE Mark for the breast cancer screening machine-learning software in October 2018. A month later, it announced that it will be testing the product in the National Health Service (NHS) as part of a larger radiology project funded by the U.K. government.
The software will be tested in collaboration with the East Midlands Radiology Consortium (EMRAD), a network of U.K. hospitals in the East Midlands region, that was granted funding through NHS England's Test Beds program. This program aims to get innovative digital technologies for tackling health and care challenges off the ground, and the grant to EMRAD is for the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve breast screening.
Because the U.K. has a shortage of radiologists, it is hard to comply with the NHS requirement for two consultant radiologists to read each mammogram, so the idea is that the software could help pick up the slack.
e-CTA CT angiography analysis software, Brainomix
Known as e-CTA, the software uses artificial intelligence to automate the assessment of collateral blood vessels on the CT angiography (CTA) scans of patients with acute stroke. The software works in conjunction with Brainomix's e-ASPECTS software to display the collateral vessels in a vivid color heat map and direct physicians to relevant findings within minutes, according to the company. Clinicians can access the results through email, a web browser interface, or DICOM.
The software delivers fast, consistent assessments of collateral vessels powered by AI and big data, based on CTA analysis, and it facilitates better-informed treatment decisions for endovascular treatment by integrating seamlessly into the clinical pathway for acute stroke treatment, including acquisition and review workstations, hospital communication systems, and other DICOM devices, the vendor noted. e-CTA received the CE Mark in May 2018.
Craniocervical CTA is the standard collateral vessel diagnostic tool for patients presenting within the first hours after the onset of clinical stroke symptoms. It is quick and readily available, making it ideal for an emergency situation, the company added.
"Experts are reading the same scans and coming to different conclusions," said Dr. Michalis Papadakis, chief executive and founder of Brainomix, in an article published on 1 April 2018 in the Times newspaper. He noted that the software can assist doctors in making decisions based on crucial brain scans of stroke patients, and it can remove some of the delays that result from the uncertainty in assessing these patients.
Best New Radiology Vendor
Kheiron Medical Technologies
"By radiologists for radiologists" is one of Kheiron Medical Technologies' slogans on its website. "Clinical responsibility, rigor, and utility guide everything we do. We work closely with radiologists to build products that help them in real-world everyday practice," it adds.
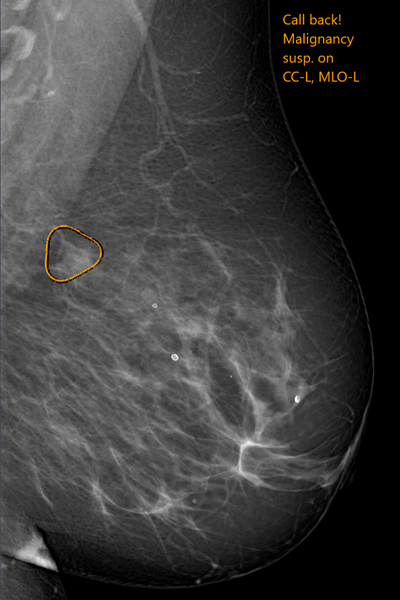
 Kheiron Medical Tehnologies' software uses deep learning to help detect malignancies in mammograms. Image courtesy of Kheiron.
Kheiron Medical Tehnologies' software uses deep learning to help detect malignancies in mammograms. Image courtesy of Kheiron.The company's software combines deep-learning methods and radiology insights to detect malignancies in mammograms. Kheiron claims to be the first U.K. company to receive a CE Mark in deep learning and radiology.
Kheiron Medical was founded in 2016 by Dr. Peter Kecskemethy and Tobias Rijken. Kecskemethy co-founded Globle Technologies, a start-up that developed mobile apps for professional networking, and worked as a freelance tech advisor and postdoctoral researcher. Rijken refers to himself as a machine-learning entrepreneur and researcher interested in deep learning, Bayesian reasoning, and reinforcement learning. Radiologist Dr. Hugh Harvey is the clinical director.
The company aims to bring together technology and radiology specialists, including deep-learning experts and engineers from the universities of Oxford, Cambridge, Edinburgh, McGill, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, University College London, and Imperial College, along with clinical academics and radiologists.
"We are militant about putting the needs of the radiologists and clinicians first, believing that only through empowering them can we improve patient outcomes," according to Kecskemethy.
ScreenPoint Medical
ScreenPoint develops deep-learning and image analysis technology for automated reading of mammograms and digital breast tomosynthesis. It seeks to exploit the latest methods in machine learning, combining these with large digital image databases and an understanding of the physics of mammogram image formation and the practicalities of the clinical deployment of mammographic image analysis.
The company has its roots in the Diagnostic Image Analysis Group (DIAG) of the Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, the Netherlands. DIAG is involved in the development of AI and deep-learning applications in medical imaging. For 25 years, breast image analysis techniques were developed by Prof. Nico Karssemeijer and his team, resulting in articles on topics including mammography CAD, breast density, breast cancer screening, breast ultrasound, MRI, and digital pathology.
"As a result of continued innovation, algorithms for detection and diagnosis of breast cancer are now reaching unprecedented levels of performance. Researchers in DIAG were among the first to publish on deep learning in mammography," ScreenPoint noted in a statement on its website.
In November 2018, ScreenPoint received 510(k) clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for its Transpara detection and decision-support software, designed to assist radiologists with reading screening mammograms. During the same month, it signed a deal with Volpara Health Technologies, allowing Volpara to deliver ScreenPoint's AI-based products to customers as part of its expanding VolparaEnterprise AI cloud ecosystem. The move is designed to enable ScreenPoint to enter the U.S. market.
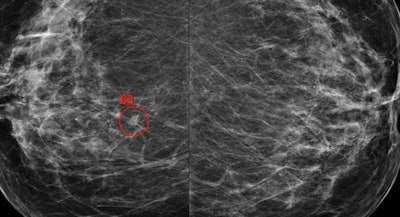 The Transpara software assists radiologists with reading screening mammograms. Image courtesy of ScreenPoint.
The Transpara software assists radiologists with reading screening mammograms. Image courtesy of ScreenPoint.Previous page | 1 | 2