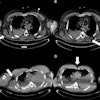
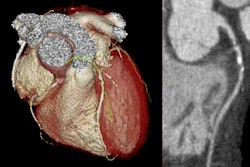
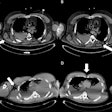
Coronary CT angiography (CCTA) is an effective way to assess risk of cardiac allograft vasculopathy in heart transplant patients, Polish researchers have reported.
A team led by Dr. Agnieszka Kuczaj of the Medical University of Silesia in Katowice found that heart transplant patients followed with CCTA exams had no adverse events. The results were published on 10 May in Transplantation Proceedings.
"CCTA offers a secure and efficient means of assessment in heart transplant recipients," the group wrote.
Cardiac allograft vasculopathy is the main cause of death after heart transplantation, Kuczaj and colleagues noted, and diagnosing the condition can be challenging. The authors investigated the safety and efficacy of CCTA in patients after heart transplant to identify any graft vasculopathy.
Their study included 107 heart transplant recipients, all of whom were three years or more post-transplant with minimal or no evidence of cardiac allograft vasculopathy in a prior CCTA exam performed at least two years before the follow-up study exam. The study period was November 2021 to August 2023; patients were included if they had an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 30 or higher, no new heart failure symptoms, and no contraindications to iodine contrast or CT scans.
Median time since transplant among study participants was seven years. Of the participants, nine showed minimal heart muscle changes on the follow-up CCTA exam, while 98 showed no changes. Among the nine with suspected cardiac allograft vasculopathy, significant heart changes were identified in eight, which led to percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty for six. Of these six, one patient died.
The investigators reported the following:
- Mean left ventricular ejection fraction at follow-up was 58%, compared with 58% at baseline.
- At follow-up, the mean estimated glomerular filtration rate was 64 mL/kg/1.73 m2, compared with a baseline value of 67.2 mL/kg/1.73 m2.
The bottom line? CCTA is a safe method of evaluating risk of cardiac allograft vasculopathy in heart transplant recipients, Kuczaj and colleagues concluded.
The complete study can be found here.