Leading Spanish experts have shared their experiences of the clinical management of breast lesions in children and adolescents. Their practical advice includes seven simple, easy-to-follow tips.
"Children usually present with benign breast lesions and management is different from adults," stated Dr. Rosa Maria Lorente Ramos, a radiologist at the Hospital Universitario Infanta Leonor, Madrid, and colleagues. "Correlation of imaging with age and clinical history and being familiar with normal development is essential for the radiologist."
Initial evaluation of breast signs or symptoms in children consists mainly of clinical assessment, and only perform ultrasound if necessary, they noted in an ECR 2023 e-poster that received a certificate of merit.
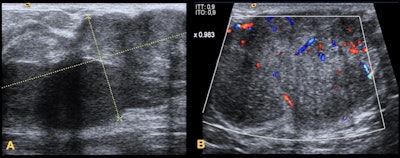 Juvenile fibroadenomas. A: Rapidly growing palpable lump in a 14-year-old girl. It appears on ultrasound as a circumscribed heterogeneous large mass. B: Palpable lump in a 13-year-old girl. It is visible on ultrasound as a circumscribed hypoechoic homogeneous mass. The lump is highly vascular on Doppler ultrasound. All images courtesy of Dr. Rosa Maria Lorente Ramos and colleagues and presented at ECR 2023.
Juvenile fibroadenomas. A: Rapidly growing palpable lump in a 14-year-old girl. It appears on ultrasound as a circumscribed heterogeneous large mass. B: Palpable lump in a 13-year-old girl. It is visible on ultrasound as a circumscribed hypoechoic homogeneous mass. The lump is highly vascular on Doppler ultrasound. All images courtesy of Dr. Rosa Maria Lorente Ramos and colleagues and presented at ECR 2023.In their exhibit, the group gave the following tips:
- Most lesions in children and young women are benign, either inflammatory or neoplastic.
- Some benign lesions tend to grow rapidly, causing huge masses.
- A new palpable breast mass is a common presenting sign of breast cancer in adults. "It is commonly said that any woman presenting with a palpable lesion should have a thorough clinical breast examination and imaging evaluation, but this is not true for children," the authors wrote.
- Initial evaluation consists mainly of clinical assessment: clinical history and physical exam.
- In children, when necessary, the initially recommended imaging technique is breast ultrasound.
- Mammograms should be performed only in patients with lesions not completely clarified by ultrasound as a complementary technique depending on initial findings and the degree of suspicion.
- Biopsy should be avoided unless necessary. It should be performed only in suspicious, large, or enlarging masses.
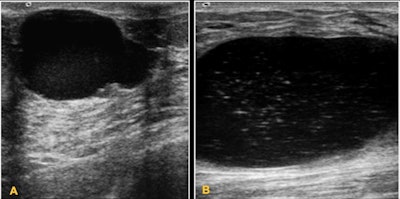 Simple cysts. (A) 13-year-old girl with a palpable lump. On ultrasound, it appears as an anechoic mass. (B) 15-year-old girl. Anechoic lesions with isolated echoes and mobile fluid level caused by debris.
Simple cysts. (A) 13-year-old girl with a palpable lump. On ultrasound, it appears as an anechoic mass. (B) 15-year-old girl. Anechoic lesions with isolated echoes and mobile fluid level caused by debris.It is important to analyze and discuss the specific management of breast lesions in children, including clinical complaints, diagnostic difficulties, imaging workup, pitfalls, and clues to differential diagnosis, according to the researchers.
Puberty development is different for both sexes. In the female breast, ductal proliferation, branching, and growth are stimulated due to estrogen. Progesterone stimulates stromal development and terminal ductal-lobular unit maturation. In the male breast, involution and ductal atrophy occur due to testosterone level increase.
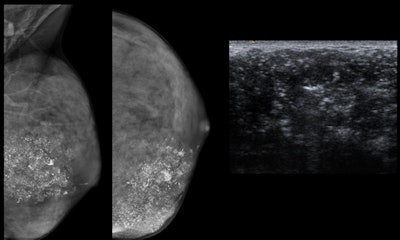 Breast cancer in an 18-year-old woman. A palpable lump can be seen on the mammogram. Dense breast (ACR D category) with regional fine pleomorphic and coarse heterogeneous calcifications. On ultrasound, a heterogeneous hypoechoic mass with irregular margins and hyperechoic calcifications is visible. The pathology is a comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ (also known as comedocarcinoma in situ), a high-grade subtype of ductal carcinoma in situ.
Breast cancer in an 18-year-old woman. A palpable lump can be seen on the mammogram. Dense breast (ACR D category) with regional fine pleomorphic and coarse heterogeneous calcifications. On ultrasound, a heterogeneous hypoechoic mass with irregular margins and hyperechoic calcifications is visible. The pathology is a comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ (also known as comedocarcinoma in situ), a high-grade subtype of ductal carcinoma in situ.The clinical signs of presentation for breast lesions or complaints are unilateral or bilateral breast enlargement, dermal lesions, palpable lumps, mastodynia, inflammatory signs, nipple discharge, and blunt or penetrating trauma, they added.
To view the whole ECR 2023 poster and learn more about the full range of cases, go to the EPOS section of the congress organizers' website.
The co-authors of the ECR e-poster were Dr. Francisco Javier Azpeitia Arman, Dr. Nicolas Rodriguez Ramirez, Dr. Ana Mercedes Perez Bartolome, Dr. Carlos Oliva Fonte, and Dr. Soledad Alonso Garcia.