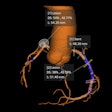
The absence of coronary artery calcium (CAC) translates into a low risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in COVID-19 patients, even in the presence of cardiac risk factors, Belgian researchers reported at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) annual congress.
CAC score evaluation in COVID-19 patients might be a useful marker for risk stratification and management, according to Dr. Andreea Motoc, cardiac imaging and research fellow at the University Hospital of Brussels, and colleagues.
Clinical value of CAC score
CAC score assessed by CT is considered a risk modifier in primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases, and it has proved to be of additional value to predict cardiovascular events, compared to classical risk factors, the authors noted in an ESC 2021 e-poster.
"Data regarding the role of CAC score in the prediction of outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients is still scarce," they explained. "We hypothesized that the absence of CAC might have an additional predictive value for an improved cardiovascular outcome of hospitalized COVID-19 patients."
To test this theory, Motoc, who is a member of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) Heart Imagers of Tomorrow (HIT) Committee, and her colleagues assessed the CAC score in 310 consecutive COVID-19 patients. They excluded 30 patients with a history of coronary artery disease. The average age of the remaining 280 patients was 63.2 years, and 57.5% were male.
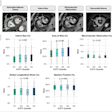
The authors used an ordinal scoring of 0 (absent), 1 (mild), 2 (moderate), or 3 (severe) for every artery. They calculated a total score by adding up the scores of each vessel and categorizing them as 0 (undetectable), 1-3 (mild), 4-5 (moderate), and greater than or equal to 6 (severe). Intra/interobserver reproducibility was evaluated in 20 randomly selected patients two weeks later.
The group then assessed the predictors of MACE. These events included heart failure, myocarditis, atrial fibrillation, acute coronary syndrome, stroke, and pulmonary embolism.
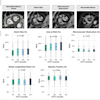
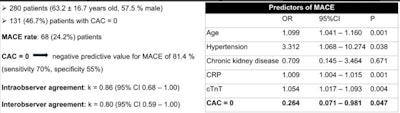 Abbreviations: cTnT = cardiac troponin test, CRP = C-reactive protein. Table courtesy of Dr. Andreea Motoc et al and the ESC.
Abbreviations: cTnT = cardiac troponin test, CRP = C-reactive protein. Table courtesy of Dr. Andreea Motoc et al and the ESC.Of the 280 COVID-19 patients, 131 (46.7%) had a CAC score of zero. MACE occurred in 68 cases (24.2%).
In patients with a CAC score of zero, the negative predictive value of MACE was 81.4%. The sensitivity was 70%, and the specificity was 55%, the authors stated.
For the intraobserver agreement, the value of k was 0.86 (95% Cl, 0.68-1.00). For the interobserver agreement, k was 0.80 (95% Cl, 0.59-1.00).
"Future directions should focus on the implementation of CAC score into mid- and long-term follow-up of this population, for a more precise and earlier estimation of cardiovascular risk," they concluded.