3D-printed models based on head CT scans may help identify optimal head positioning for intratympanic steroid injections, according to an article published online on 24 September in Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery.
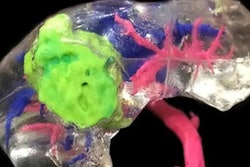
Researchers from Israel obtained CT scans of a healthy individual, segmented the temporal bone and surrounding soft tissue from the scans, and then reconstructed the scans into a virtual 3D model. After creating the individually tailored model with 3D printing, the researchers performed a simulation of steroid injections to the middle ear cleft.
They found the model yielded an optimal head positioning of 53° of rotation away from the injected ear (yaw), 27° of rotation toward the noninjected ear (roll), and 10° of transverse neck extension (pitch).
The measurements obtained from the 3D-printed model revealed the ideal patient head positioning for effective drug delivery after intratympanic steroid injection to the middle ear and also that maintaining an erect head position optimized subsequent steroid delivery from the middle ear to the inner ear, first author Dr. Omer Ungar and colleagues from Tel Aviv University noted.