Dear Advanced Visualization Insider,
A new multitasking algorithm automatically sorts through lung cancer screening studies, measuring nodule volumes and assessing potential malignancy, according to a study in the International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery.
Apart from nodule size, the biggest single determinant of malignancy, the study team found measurable improvement in predicting malignancy using image features alone. Find out how they did it here.
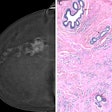
In breast cancer screening, new research from Scotland found success with texture analysis of breast cancer lesions that distinguished different cancer types. In a nutshell, the entropy-based features had different internal enhancement patterns that were strongly correlated to lesion type.
Among other findings, feature values were different between lobular and ductal carcinomas, and hormone receptor-positive (HR+) cancers had lower entropy values than HR- cancers, according to the study team. Learn more in an article you'll find here.
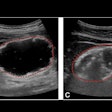
It's not often that ultrasound-based computer-aided detection (CAD) rises to the top, but Korean researchers reported in the European Journal of Radiology that their CAD algorithm can reliably characterize thyroid nodule calcifications, and, by doing so, point the way to a diagnosis of malignancy or benignity. Get the rest of the story by clicking here.
Last month, a Frankfurt meeting on catheter interventions included a presentation on the use of both echocardiography and CT data to print 3D hearts. The investigators are convinced this is the first use of a hybrid 3D printing technology.
Reliance on two modalities rather than one makes the data more accurate before it gets printed into a 3D model, say the researchers, who are planning to incorporate a fourth modality as soon as possible. Learn more about their plans by clicking here.
In cardiac imaging, the always-impressive German team responsible for pushing the envelope in high-field MRI has reported on its successful implementation of sodium-based imaging of the myocardium. Compromised cellular integrity in myocardial tissue, which shows up in high-field sodium imaging, is a strong sign of impaired ion homeostasis and cell membrane integrity, the authors explained. Increased intracellular sodium concentrations speak volumes about reduced sodium-potassium pump efficiency, in an article you'll find here.
For the latest advanced imaging developments in Europe, your Advanced Visualization Community is the place to bookmark.