BOSTON - One of the largest virtual colonoscopy (VC or CT colonography [CTC]) trials ever aimed at a higher-risk screening population has yielded good results across 12 sites in Italy.
Despite the investigators' lack of stringent entrance criteria -- participating centers needed only a multidetector-row CT scanner and experience on 50 VC cases -- accuracy was acceptable to excellent compared to optical colonoscopy in nearly 1,000 patients who completed both exams.
Sponsored by the Società Italiana di Radiologia Medica (SIRM), the 600,000-euro trial was funded by the private foundation Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC), Fondazione CRT, and Regione Piemonte, said principal investigator Dr. Daniele Regge, who presented the first results of the study on Tuesday at the International Symposium on Virtual Colonoscopy.
"The aim of the study was to assess the sensitivity and specificity of CTC in a population at increased risk for colorectal cancer from personal or family history with double-checked colonoscopy as the standard of reference," said Regge, who is a radiologist at the Institute for Cancer Research and Treatment (IRCC) in Candiolo (Turin), Italy.
A higher-risk cohort
Of the 934 asymptomatic subjects who completed both VC and colonoscopy, 373 (40%) had a family history of colorectal polyps or cancer, 341 (36%) had a previous polypectomy, and 220 (24%) had a positive fecal occult blood test result.
"Keep in mind that Italy is smaller than California, with about a sixth of the population of the U.S., so one of the problems was finding enough centers that could adequately participate in the study," Regge said. "For this reason, we kept our entry requirements pretty low."
If not state-of-the-art, the technical requirements were carefully considered to make the best of the budget and the need for wide participation. Investigators needed only a four-slice CT scanner or better, though 10 of 12 participating centers had at least a 16-slice machine. They also needed experience on 50 VC cases, 2D/3D VC interpretation software, onsite experienced gastroenterologists to confirm the accuracy of the virtual exams, and a minimum of one case accrual per month.
The centers were also free to choose their cathartic bowel prep agents from a menu that included 4 L of polyethelyne glycol lavage, Phospho-soda derivatives, senna derivatives, and polyetheylene glycol or Phospho-soda derivatives plus iodinated contrast agents. Only about a third of the participants had fecal tagging, he said.
Colonic insufflation consisted of CO2; or air, detector collimation had to be set at 2.5 mm or narrower, and the low-dose protocol required mAs of 50 or less, Regge said.
"Planning was performed during the (patient) interview," Regge said. "Patients came back for CTC and most underwent same-day conventional colonoscopy. So there were quite a few points where patients could drop out of the study."
In fact, 76 withdrew before completing both tests. In addition, VC was not performed in eight subjects, colonoscopy was not performed in nine, and colonoscopy was incomplete in another 36 (4%). Subtracting another three patients in whom histology was unavailable, the total number of cases evaluated was 934 of 1,066 or 88% of the original cohort.
An "intention-to-treat" approach to statistical analysis meant that patients with a poor bowel prep went ahead with scanning and colonoscopy, Regge said. All results were analyzed both per patient and per polyp with colonoscopy.
For a given polyp to be considered a true-positive match between VC and optical colonoscopy, it had to appear within the same or adjacent colonic segment, and the two recorded diameter measurements had to be within 50% of each other. Matching was performed prospectively, following segmental unblinding of conventional colonoscopy results.
Virtual colonoscopy was deemed positive when at least one lesion 6 mm or larger was detected by the test. Sensitivity and specificity were calculated by using 2 x 2 contigency tables. All data were analyzed centrally at Regge and colleagues' facility in Candiolo.
As for the 25 readers, 11 had experience in 50 to 100 exams, nine had experience in 100 to 500 VC exams, and five had performed more than 500 virtual colonoscopies, Regge said. About two-thirds of the cases were read with primary 2D (68.6%, n = 641), which required a mean of 19 minutes reading time, compared with primary 3D (25.2%, n = 235) at a mean of 22 minutes.
The results
"We had 327 polyps 6 mm or larger, most were adenomas (76%, n = 248), and we had 42 cancers, and the average lesion diameter was 14 mm," Regge said. Advanced histology was found in 187 polyps, including 66 lesions 6 mm to 9 mm, and in 121 lesions larger than 10 mm. There were three cancers 6 mm to 9 mm in size (2%), and 39 (24%) larger than 10 mm.
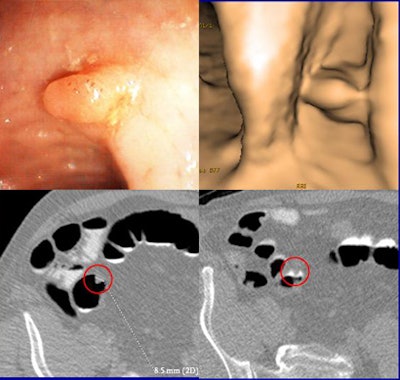 |
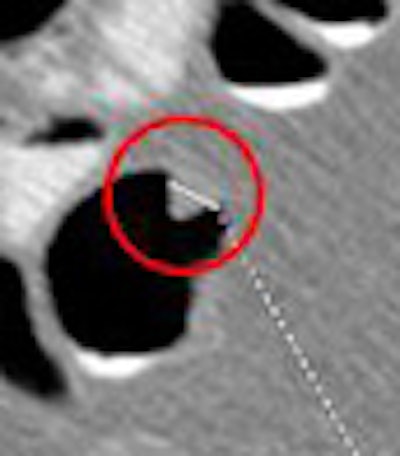
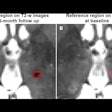
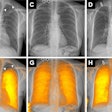
| VC and colonoscopy both detected an 8.5-mm sessile lesion that was removed at colonoscopy and proved to be an adenocarcinoma. The 58-year-old male patient had a family history of colorectal cancer. Clockwise from upper left are endoscopy image, 3D VC, and 2D axial views (bottom). All images courtesy of Dr. Daniele Regge. |
Virtual colonoscopy missed two cancers larger than 1 cm, though it found all of the small ones, Regge said. Both of the cancers were visible retrospectively on the CT data, he said, so these important misses might be attributed to a lack of training.
Owing to the higher-risk population, the prevalence of advanced neoplasia was about 19% of all lesions 6 mm or larger.
While the matched per-polyp sensitivity was 84% for lesions 1 cm and larger, it dropped to 53% for medium-sized lesions 6 mm to 9 mm. Per-patient sensitivity/specificity for detecting all adenomas and cancers 6 mm or larger and 10 mm or larger were 84.2%/90.4% and 90.7%/84.6%, respectively.
Perhaps the most interesting results were in the 341 postpolypectomy subjects, "because this is an area that has not been well studied by the literature," Regge said. In this subgroup, per-patient sensitivity/specificity for detecting all adenomas and cancers 6 mm or larger and 10 mm or larger were 83.0%/89.2% and 89.3%/84.0%, respectively.
The main limitation in the study was likely the lack of training, for which requirements were kept low to encourage participation, Regge said. "We did not only have research institutions in the study but also busy hospital wards, so these are realistic results," he said. The same restraints probably kept the accrual rate relatively slow, he added.
"Nevertheless, we feel the results are good, they're in agreement with the ACRIN (6664) group, but on a different population," he said. "And we should think about introducing CTC as an alternative to colonoscopy in patients with increased risk, for example for surveillance for family history," he said. "And certainly this study has contributed to the diffusion of CTC in Italy."
In response to an audience question, Regge said that low sensitivity in the 6-mm to 9-mm range might be attributable to the target-rich population.
"We know that most of these cases are patients with lots of polyps. We know if you have 20 polyps, you're bound to miss some. This does not modify the per-patient sensitivity, but it does influence the per-polyp sensitivity," he said.
"I thought the results were really excellent considering how different the patient population is compared to the Pickhardt trial and the ACRIN (6664) trial," commented Dr. Ronald Summers from the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, MD, noting that the study will constitute one of the largest populations of above-average risk VC cohorts in the literature.
The 341 postpolypectomy patients are certainly among the largest VC surveillance populations to date, and the results suggest that VC is well-suited to the task, Regge said.
By Eric Barnes
AuntMinnie.com staff writer
October 17, 2007
Related Reading
Positive trial results boost VC's prospects for broader screening role, October 16, 2007
ACRIN trial shows VC ready for widespread use, September 28, 2007
Study of two large screening cohorts favors VC over OC, October 4, 2007
Study: primary 3D VC equivalent to colonoscopy, September 12, 2007
Gastroenterologists plan to perform VC, January 25, 2007
Polyp surveillance risk may be acceptably low, October 17, 2007
Copyright © 2007 AuntMinnie.com